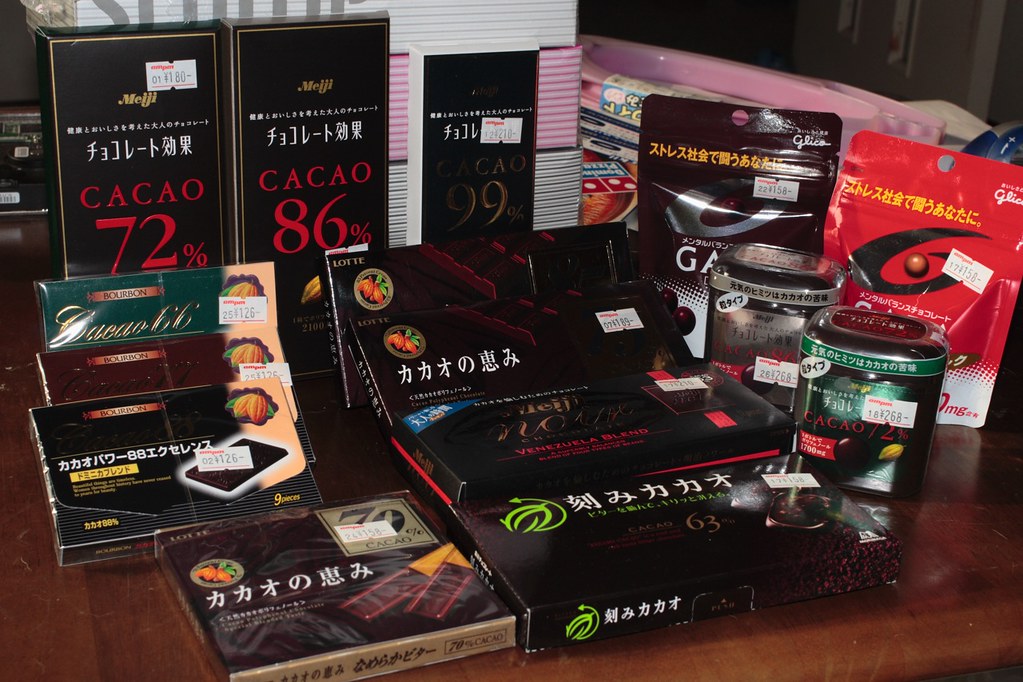
The chocolate industry plays a pivotal role in the economies of developing and emerging countries. This industry is a significant contributor to these countries’ gross domestic product (GDP), providing income to farmers, creating jobs, and attracting investment. It is not just about the sweet indulgence that many enjoy worldwide, but it’s also about the economic impact, the livelihoods supported, and the development stimulated in these countries. This article aims to delve into the contribution of chocolate to these economies, shedding light on the economic impact of cocoa production, the increasing demand for chocolate in emerging markets, employment opportunities in the chocolate industry, the role of trade, and export of chocolate products, as well as the challenges faced by chocolate-producing countries.
The chocolate industry, centered around the cultivation of the cocoa plant and the production of chocolate products, is a critical sector in many developing and emerging economies. From small-scale farmers who grow cocoa plants to large companies that produce and distribute chocolate products around the globe, the chocolate industry involves a wide array of actors and processes. In recent years, the demand for chocolate has seen a significant surge, especially in emerging markets, leading to increased economic activity and growth in these regions. However, this growth also brings with it numerous challenges – from environmental issues to market volatility – that these countries must navigate. In this article, we will explore these various aspects and delve into the importance of the chocolate industry to the economies of developing and emerging countries.
The Growing Demand for Chocolate in Emerging Markets



Emerging markets have shown a significant increase in chocolate demand in recent years.This surge in demand has led to a corresponding rise in cocoa prices due to the balance of supply and demand. Countries known as the BRICs (Brazil, Russia, India, and China) are expected to see an increase in chocolate consumption between 20% and 40% by 2018. However, it’s essential to note that per capita chocolate consumption in these emerging markets is relatively low compared to more developed regions. For instance, the average per capita annual chocolate consumption in China is just 4 ounces, while Europeans consume an average of 17 pounds per year.
One of the emerging markets where the demand for chocolate is rapidly rising is China. Increased disposable incomes and a growing middle class have led to a surge in demand for luxury goods, including chocolate. Chocolate companies, both domestic and international, have responded to this trend by expanding their operations in China. They are focusing not only on the major cities but also on smaller towns and rural areas where chocolate consumption still has considerable room for growth. This expansion into previously untapped markets presents a significant growth opportunity for the chocolate industry and contributes to the economic development of these areas.
Moreover, the growing demand for chocolate in emerging markets like the BRICs is not just driven by increasing incomes but also changes in consumer tastes and preferences. With globalization and the influence of western culture, consumers in these markets are developing a taste for western-style confectionery, including chocolate. This shift in consumer behavior is creating new opportunities for chocolate manufacturers, who are now catering to a rapidly growing customer base with different tastes and preferences.
The Economics of Cocoa Production
Cocoa production is a crucial economic activity in many developing and emerging countries, contributing significantly to revenue generation and job creation. The cultivation of cocoa provides a livelihood for millions of individuals and communities, particularly in rural areas. However, the cocoa market is characterized by volatility, with cocoa prices experiencing significant fluctuations since 2014. Factors like supply chain disruptions, market trends, and even disease outbreaks can influence cocoa prices [2].
Take the case of Ivory Coast, the world’s largest cocoa producer. Cocoa accounts for a significant portion of the country’s export revenue, making it a cornerstone of the country’s economy.Cocoa farming provides a source of income for millions of farmers in the country. However, the volatility of cocoa prices can have profound impacts on these farmers’ livelihoods. When prices are low, farmers struggle to make a living, and some may be forced to switch to other crops or abandon farming altogether. This not only affects the farmers and their families but also has broader implications for the economy of the country.
The economic benefits derived from cocoa production are not without challenges. Cocoa prices have been highly volatile since 2014, with sharp spikes and drops. This volatility is influenced by various factors such as supply and demand dynamics, global market trends, and local factors. For instance, the Ebola outbreak in West Africa caused a significant spike in cocoa prices due to fears of supply chain disruption. While this price spike was beneficial for cocoa traders and speculators, it created uncertainty and challenges for cocoa farmers. The complexity and volatility of the cocoa market underscore the need for robust mechanisms to stabilize cocoa prices and provide a fair income for farmers.
The Complex Supply Chain of Cocoa
The supply chain involved in cocoa production and chocolate manufacturing is complex and multifaceted. It involves multiple steps, from the cultivation of cocoa trees to the processing of cocoa beans to the production of chocolate products. Each of these steps involves different actors, including farmers, traders, processors, manufacturers, and retailers. Global businesses and commodities traders play a crucial role in the cocoa market, participating through futures contracts. They have a profound influence on cocoa prices and market dynamics.
The cocoa supply chain starts with the farmers who cultivate the cocoa trees. Once the cocoa pods are harvested, they need to be fermented and dried before the beans can be sold. This process requires careful monitoring and expertise to ensure the quality of the beans. After the beans are dried, they are typically sold to traders who then sell them to chocolate manufacturers. This process involves multiple intermediaries and can be subject to price fluctuations and quality variations. Efficient supply chain management is crucial to ensure the timely delivery of cocoa beans to manufacturers and to maintain the quality and consistency of the final chocolate product.
However, the complexity of this supply chain also presents numerous challenges. For instance, the long and often opaque supply chain can make it difficult for consumers and businesses to trace the origin of the cocoa beans and ensure they are sustainably and ethically sourced. In response to these concerns, some chocolate manufacturers and retailers have started implementing traceability and sustainability initiatives. These initiatives aim to provide greater transparency in the cocoa supply chain and ensure that cocoa farmers receive a fair price for their produce.
Cocoa Production and Climate
Cocoa trees are inherently sensitive to changes in climate, requiring specific temperature and rainfall conditions to thrive. As such, changes in climate patterns can significantly affect cocoa production, potentially leading to lower yields and impacting farmers’ livelihoods in cocoa-producing countries. Additionally, local factors such as political instability and labor conditions can also influence cocoa prices. These challenges underscore the need for sustainable farming practices and climate resilience in the cocoa sector.
One of the regions most affected by the impact of climate change on cocoa production is West Africa, which accounts for a significant portion of global cocoa production. Rising temperatures and changing rainfall patterns have made it increasingly challenging to cultivate cocoa trees in this region. Cocoa farmers are facing difficulties maintaining their cocoa farms, and both the quality and quantity of cocoa beans have been affected. To combat this crisis, initiatives such as agroforestry and climate-resilient farming practices are being implemented to help farmers adapt to changing climatic conditions and ensure the sustainability of cocoa production.
However, adapting to climate change is not the only challenge. Cocoa production is also susceptible to pests and diseases, which can lead to significant crop losses. Efforts are being made to develop disease-resistant cocoa varieties and implement effective pest management strategies. Moreover, socio-economic factors such as labor conditions, income inequality, and access to resources also play a crucial role in the sustainability of cocoa production. Addressing these issues is vital to ensure the long-term viability of the cocoa sector and its contribution to the economies of developing and emerging countries.
The Role of Chocolate in Employment and Trade
The chocolate industry plays a vital role in providing employment opportunities in developing and emerging countries. From farming and processing to manufacturing and retail, the industry supports a wide range of jobs. In many of these countries, cocoa cultivation is a major source of income for rural communities, contributing to poverty reduction and economic development. Moreover, the trade and export of chocolate products contribute significantly to the economies of these countries, driving growth and facilitating their integration into global markets.
Ghana, the second-largest cocoa producer in the world, serves as a prime example of the employment opportunities provided by the chocolate industry. Cocoa farming is a significant source of income for millions of Ghanaians, and the industry provides employment for both skilled and unskilled workers. Besides farming, the chocolate industry also creates jobs in cocoa processing, chocolate manufacturing, and retail.The export of Ghanaian cocoa and chocolate products contributes to the country’s economy and helps promote economic development.
The chocolate industry also plays a significant role in trade, with cocoa beans and chocolate products being major export commodities for several developing and emerging countries. The revenues generated from the export of these commodities contribute significantly to these countries’ GDP and foreign exchange earnings. Moreover, the chocolate industry also attracts investment, both domestic and foreign, further contributing to economic growth and development.
The Globalization and Localization of the Chocolate Industry
Globalization has significantly impacted the chocolate industry, leading to the expansion of markets and providing access to consumers worldwide. The cocoa-chocolate value chain is characterized by a south-to-north orientation, with cocoa production predominantly taking place in developing countries, while the manufacturing of chocolate products is often centralized in richer countries [4]. However, the influence of localization in the industry is equally important, as consumer perceptions of chocolate quality and taste are often shaped by their local experiences and preferences.
The trend of single-origin chocolates exemplifies the interplay of globalization and localization in the chocolate industry. These chocolates, made from cocoa beans sourced from a specific region or country, cater to consumers’ growing interest in unique flavors and experiences. By highlighting the origins of the cocoa beans, chocolate manufacturers can tap into consumers’ desire for authenticity and uniqueness, allowing them to connect with consumers on a more personal level and cater to their preferences. This strategy of localization allows for greater diversity and innovation in the industry, contributing to the growth and evolution of the chocolate market.
Moreover, the globalization of the chocolate industry has led to the spread of chocolate consumption to new markets. Developing and emerging countries, which were once primarily producers of cocoa, are becoming significant consumers of chocolate products. This shift is driven by factors such as increasing incomes, changing tastes, and the influence of western culture. As a result, chocolate manufacturers are adapting their products and marketing strategies to cater to these new consumers, further driving the growth and dynamism of the global chocolate industry.
The Future of the Chocolate Industry
The chocolate industry shows promising potential for future growth, with regions like East Asia and Africa emerging as major players. These regions present significant growth opportunities in terms of both cocoa production and chocolate consumption. East Asia, particularly China and India, with their large populations and growing middle classes, is poised to become a significant market for chocolate products. Meanwhile, Africa, with its conducive climate for cocoa cultivation and growing population, has the potential to increase its share in global cocoa production.
However, this potential for growth does not come without challenges. The dynamics of the global chocolate market are changing, and the industry needs to adapt to these changes. European chocolate companies, which have traditionally dominated the industry, could face increasing competition from Asian conglomerates and African cocoa producers. Moreover, the need for sustainable and ethical practices in cocoa production is becoming increasingly important. This is driven by growing consumer awareness of environmental and social issues, as well as regulatory pressures.
One of the trends shaping the future of the chocolate industry is the increasing demand for premium and specialty chocolates. With growing consumer sophistication and a willingness to pay a premium for quality, chocolate manufacturers have the opportunity to innovate and differentiate their products. This trend towards premiumization is not just about offering higher-quality products, but also about providing a unique and memorable chocolate experience. Manufacturers that can cater to this demand stand to benefit from higher profit margins and a loyal customer base.
Integration of Chocolate-Producing Countries into Global Markets
The integration of chocolate-producing countries into global markets is influenced by a variety of factors, including government regulations, market dynamics, and consumer preferences. Governments often implement regulations on cocoa production and trade to ensure quality, safety, and fairness in the industry.The integration of certain countries into regional blocs such as the European Union has resulted in changes to regulations and market dynamics, leading to debates over the definition of “chocolate” and the standardization of quality.
The liberalization of markets and the shift towards market-driven price setting have also influenced the integration of chocolate-producing countries into global markets. These changes have led to greater competition and efficiency in the industry, but they have also posed challenges, such as price volatility and the marginalization of small-scale farmers. Moreover, increased consumer awareness of labor conditions and low incomes in cocoa production has led to pressure on chocolate companies to ensure the sustainability and ethical sourcing of their cocoa.
One of the key aspects of the integration of chocolate-producing countries into global markets is the role of trade policies and regulations. Governments often implement trade policies to protect their domestic industries, regulate exports and imports, and ensure fair trade practices. However, these policies can also create barriers to trade and limit the access of chocolate-producing countries to global markets. As such, the negotiation of trade agreements and the harmonization of trade policies are crucial to facilitate the integration of chocolate-producing countries into global markets.
Health Perceptions and Consumer Behavior in the Chocolate Market
Consumer perceptions about the health effects of chocolate have significantly changed over time. While chocolate was once associated with indulgence and guilty pleasure, it is now increasingly seen in a positive light due to its potential health benefits. However, this positive perception is often