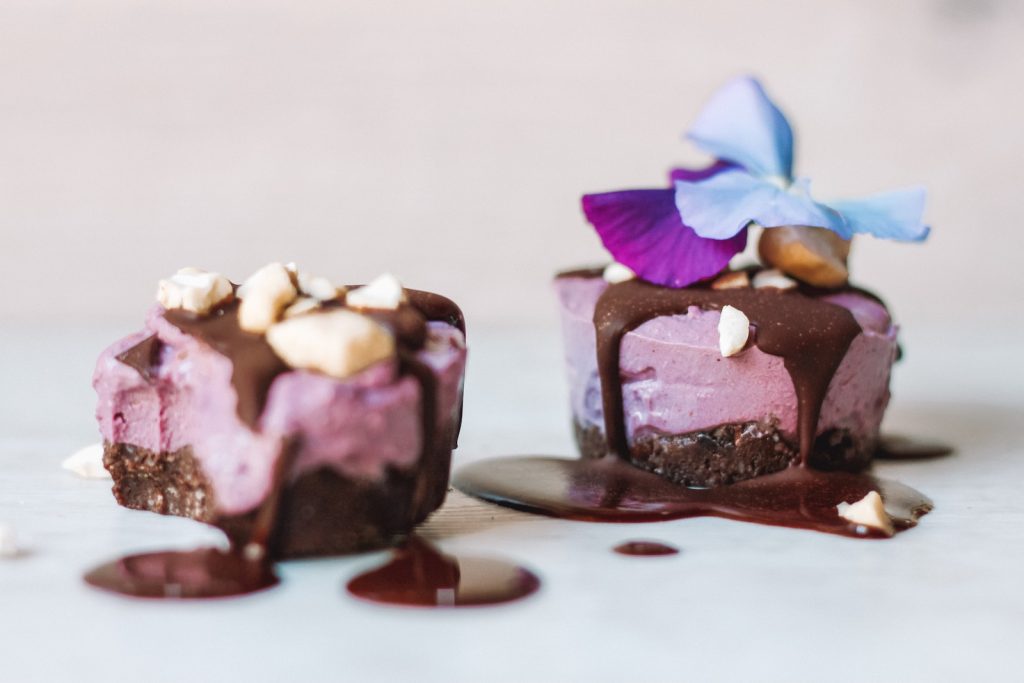
In the realms of confectionery, chocolate reigns supreme due to its rich, comforting taste and the tapestry of history woven into its existence. As culinary philosophies evolve, veganism has emerged to challenge traditional chocolate-making methodologies, infusing the age-old indulgence with modern sensibilities. Vegan chocolate is more than a mere confection; it’s a reflection of a lifestyle choice that emphasizes ethical consumption and environmental sustainability. In delving into the essence of vegan chocolate, we traverse the journey from cacao bean to the quintessential vegan chocolate bar, demystifying what vegan chocolate entails.
The Underpinning Philosophy



The vegan movement fundamentally opposes the use and exploitation of animals. This ethos extends to every sphere of consumption, including the cherished realm of chocolate. Traditional chocolate often contains milk or milk derivatives which are eschewed in the vegan philosophy. Therefore, vegan chocolate is formulated to exclude any animal-derived ingredients.
- Ethical sourcing of ingredients: Vegan chocolate makers often prioritize the ethical sourcing of cacao beans and other ingredients, aligning with the broader vegan ethos of minimizing harm and promoting sustainability.
- Environmental consciousness: The production of vegan chocolate tends to have a smaller carbon footprint, as plant-based ingredients generally require less resource-intensive cultivation compared to animal-based ingredients.
Ingredients Alchemy
At the heart of vegan chocolate is the cacao bean, the genesis of all chocolate. However, the journey from bean to bar in the vegan paradigm omits the customary milk, instead, harnessing a medley of plant-based ingredients.
Plant-based Milk Alternatives
The omission of dairy is a defining characteristic of vegan chocolate. However, achieving a similar creaminess to that of milk chocolate is a quest that beckons alternative solutions. Here, almond, soy, and coconut milk emerge as popular harbors.
- Almond Milk: Almond milk carries a subtle nutty flavor and a creamy consistency. When amalgamated into the chocolate-making process, it can lend a delicate richness, without overshadowing the robustness of cacao. Moreover, its relatively low calorie and fat content compared to traditional milk, make it a sought-after alternative among health-conscious consumers.
- Soy Milk: Known for its smooth texture and balanced nutritional profile, soy milk serves as a remarkable substitute. Its inherent creaminess resembles that of dairy milk, making it a favorable choice for vegan chocolate makers aiming to replicate the traditional milk chocolate mouthfeel.
- Coconut Milk: The richness of coconut milk, accompanied by its tropical hint, brings a unique flavor profile to vegan chocolate. Its high-fat content ensures a luxurious texture, which can be particularly appealing in a creamy vegan milk chocolate formulation.
Image: almond milk is one ingredient of vegan choclate.
Sweeteners
The sweetening agents in vegan chocolate are meticulously chosen to avoid the common industry practice of utilizing bone char in sugar processing. This highlights the extent to which vegan chocolate makers go to ensure the integrity of their products.
- Coconut Sugar: Derived from the sap of coconut palm trees, coconut sugar is a less processed sweetener that retains some nutrients. Its low glycemic index and subtle caramel undertone make it a favorable choice for those seeking a less refined sweetening agent.
- Agave Syrup: Agave syrup, with its sweet, mild taste, is an excellent sweetener for vegan chocolate. It dissolves easily, making it a convenient choice in the chocolate-making process. Furthermore, its sweetness potency allows for less quantity to achieve the desired sweetness, potentially reducing the overall sugar content.
- Maple Syrup: The distinct, robust flavor of maple syrup can add a new dimension to the taste profile of vegan chocolate. Besides its flavor, maple syrup’s mineral content, including calcium, potassium, and magnesium, presents a marginal nutritional advantage over conventional sugar.
The dialogue between plant-based milk alternatives and sweeteners is a dance of culinary innovation and ethical commitment. It’s a testament to how vegan chocolate makers are pushing the boundaries to craft products that not only satisfy ethical and dietary preferences but also the discerning palates of chocolate aficionados.
The Crafting Process
The crafting of vegan chocolate follows a meticulous pathway to ensure adherence to vegan principles while not compromising on taste and texture. The process begins with the harvesting of ethically sourced cacao beans, followed by fermentation, drying, and roasting to develop the nuanced flavors characteristic of premium chocolate.
Stone Grinding
Stone grinding is an age-old technique, revered for its ability to yield a smoother texture in the resultant chocolate. This process begins with the cacao beans being meticulously cleaned to ensure no foreign particles are present. Following this, the beans are subjected to grinding under or between stone wheels or disks. The friction and pressure generated during this process cause the cacao beans to break down into smaller particles, eventually forming a fine paste.
- Particle Size Reduction: The primary objective of stone grinding is to reduce the particle size of the cacao beans, and other added ingredients like sugar or plant-based milk powders, to such an extent that they become a homogenous paste. A smaller particle size is instrumental in achieving the desired smooth texture in the final chocolate product.
- Heat Generation: The friction during stone grinding generates heat, which in turn aids in the release of the cocoa butter inherent in the cacao beans. This natural fat acts as a binding agent, helping in creating a cohesive mixture alongside the other plant-based ingredients.
- Flavor Development: Additionally, stone grinding initiates the journey of flavor development. The gradual breakdown of the cacao beans unveils the initial layer of chocolate’s complex flavor profile.
Conching
As the cacao paste emerges from the stone grinding phase, it enters the realm of conching, a process named after the conch-shell like shape of the original vessels used. Conching is a prolonged procedure, often lasting several hours to even days, where the chocolate paste is continuously aerated and agitated.
- Texture Refinement: The primary aim of conching is to further refine the texture of the chocolate. The continuous kneading and aerating actions during conching help to smooth out any remaining rough particles, ensuring a silky mouthfeel in the final product.
- Flavor Enhancement: Conching is also a playground for flavor development. The aeration helps in evaporating any unwanted acidic or bitter compounds, while the agitation aids in well-blending the ingredients, both of which contribute to a well-rounded flavor profile.
- Temperature Control: Throughout conching, temperature control is crucial as it influences the texture and flavor. A well-managed temperature ensures that the chocolate remains in a liquid state for effective aeration and mixing, setting the stage for a well-tempered finished product.
These labor-intensive, time-honored processes of stone grinding and conching are where the magic truly happens, transmuting humble cacao beans and plant-based ingredients into a vegan chocolate bar ready to tantalize the taste buds. Through these steps, vegan chocolate makers are able to craft products that bear the hallmark of quality, delivering a sensory delight that is at par with, or even superior to traditional chocolate.
Flavor Spectrum
The flavor profile of vegan chocolate can rival that of traditional chocolate, offering a diverse spectrum of tastes and textures. The purity of cacao shines through, accentuated by the varied plant-based ingredients each brand incorporates. From the dark, intense flavors of high-cacao content bars to the sweet, creamy essence of vegan “milk” chocolates, there is a vegan chocolate to satisfy every palate.
Brands Leading the Charge
Several brands have embraced the vegan chocolate movement, each with their own unique interpretation of this ethical indulgence.
Trailblazing in Ethical Indulgence
In the modern era of conscientious consumption, a select cadre of chocolate brands has emerged at the forefront, blending age-old chocolate-making traditions with contemporary ethical and sustainable practices. Among them, Endorfin Foods, Raaka, and Taza Chocolate stand as paragons of vegan chocolate craftsmanship. Each of these pioneers has taken a distinctive route towards creating exquisite vegan chocolates while championing the principles of ethical sourcing and environmental stewardship.
- Endorfin Foods: Embodying a philosophy of honoring the ancient tradition of chocolate-making while embracing modern ethical standards, Endorfin Foods crafts vegan chocolates that are a tribute to purity and sustainability. Their unique approach is reflected in the usage of wholesome, organic ingredients and a commitment to maintaining a traceable supply chain. By sourcing cacao from small-scale farmers and ensuring fair trade practices, Endorfin Foods exemplifies a model of responsible chocolate-making that resonates with the ethos of discerning vegan consumers.
- Raaka: With transparency at its core, Raaka extends an invitation to chocolate aficionados to experience chocolate in its unadulterated form. Renowned for its unroasted, or ‘virgin’ chocolate, Raaka takes a minimalist approach, allowing the true essence of cacao to shine through. This brand is also steadfast in its commitment to fair trade and direct trade practices, forging close partnerships with cacao farmers to ensure a fair remuneration and nurturing a culture of mutual respect and sustainability.
- Taza Chocolate: Taza Chocolate is synonymous with stone-ground chocolate, a nod to traditional Mexican chocolate-making techniques. Their chocolate bars boast a rustic, gritty texture, a delightful departure from the overly refined chocolates that crowd the market. The cornerstone of Taza’s operation is its Direct Trade Certification Program, a testament to its dedication towards ethical sourcing and forging a direct connection with cacao farmers. By sidestepping the conventional fair trade certification and opting for a more personal, relationship-driven approach, Taza ensures a higher standard of ethical practice and quality.
The narratives of Endorfin Foods, Raaka, and Taza Chocolate are not just about scrumptious vegan chocolates; they embody a larger narrative of mindful consumption. Each brand, with its unique narrative and approach, contributes to a burgeoning market of vegan chocolate that appeals to both the palate and the conscience. Through their endeavors, these brands are crafting a new legacy of chocolate-making, one that honors the sanctity of nature, the dignity of every individual in the supply chain, and the discerning taste of the modern consumer. This burgeoning domain of ethical indulgence is a testament to the evolution of chocolate from a mere sweet treat to a medium of expressing one’s values and making a positive impact on the globe.
The Verdict
Vegan chocolate transcends the realm of mere confectionery, embodying a lifestyle committed to ethical and environmental principles. As a connoisseur of chocolate, embracing the vegan variant is not only a nod to evolving culinary ethos but also an exploration into a rich tapestry of flavors and textures rooted in compassion and sustainability. The essence of vegan chocolate is a testament to the harmonious fusion of tradition with modernity, epitomizing the ever-evolving narrative of chocolate in contemporary society.