Sensory science plays a pivotal role in deciphering and understanding the sensory properties of chocolate, impacting its taste, aroma, texture and appearance. This involves employing sensory evaluation techniques to assess the quality and consumer perception of various chocolate products. This understanding of the sensory aspects of chocolate is not merely important but essential for the chocolate industry. It guides the industry to innovate and create chocolate products that align with consumer expectations, thereby ensuring customer satisfaction and driving the success of their business.
This introduction to the world of chocolate sensory science isn’t complete without emphasizing the unique place chocolate holds in our lives. This popular treat, whether in the form of a rich, dark chocolate bar or a creamy milk chocolate truffle, is cherished by people across the globe. The sensory experience of chocolate is undeniably part of its charm. From the moment you unwrap a piece of chocolate and take that first bite, your senses are engaged. The aroma wafts up, the smooth texture melts on your tongue, and the taste lingers on your palate. The experience is a symphony of sensory delights. But did you ever wonder how chocolate manufacturers ensure that each piece of chocolate delivers a consistent and enjoyable sensory experience? This is the realm where sensory science shines, offering tools and techniques to create a memorable and consistent sensory experience with each bite.
Importance of Sensory Science in the Chocolate Industry



In the dynamic and competitive chocolate industry, sensory science stands as a pillar of quality control and product innovation.It provides objective measurements and evaluations of the sensory attributes of chocolate. Sensory science aids in identifying and analyzing the taste, aroma, texture, and appearance of chocolate – the key attributes that contribute to its overall quality. By using sensory science, chocolate manufacturers can innovate and develop new flavors and products based on consumer preferences. This understanding of sensory properties empowers the industry to make informed decisions regarding product development, marketing, customer satisfaction, and overall business strategy.
For instance, sensory science enables chocolate manufacturers to create products that not only taste good but also appeal to the senses. By conducting sensory evaluations, they can collect data on the sensory attributes of chocolate, such as its sweetness, bitterness, and aroma. This information can then be used to develop products that meet consumer expectations and preferences. For example, if a certain segment of the population prefers a sweeter chocolate, manufacturers can adjust the formulation to achieve the desired level of sweetness. If consumers show a preference for a more intense cocoa flavor, manufacturers can explore different roasting techniques to achieve that desired flavor profile.
In addition, sensory science provides a framework for continuous improvement and innovation. By identifying and analyzing the sensory attributes that are most valued by consumers, chocolate manufacturers can focus their research and development efforts on these areas. This could involve experimenting with new ingredients, refining existing recipes, or developing new processing techniques. Sensory science also supports the chocolate industry in remaining competitive by enabling it to adapt to changing consumer tastes and preferences.
Sensory Evaluation and Chocolate Quality
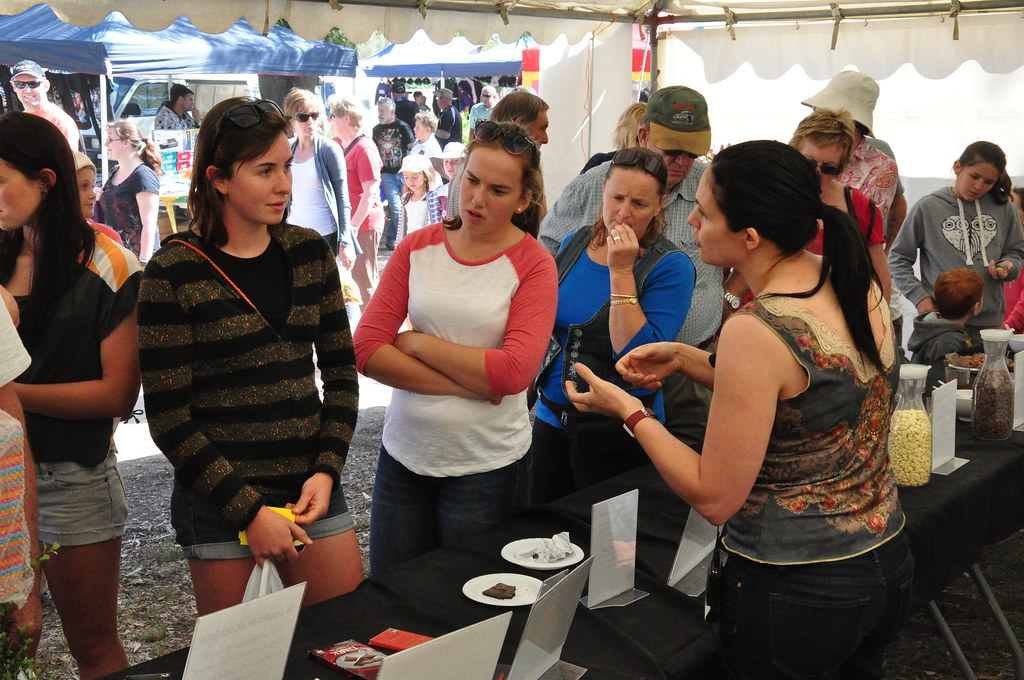
Sensory evaluation stands as a key tool in assessing and ensuring the quality of chocolate. It involves trained panelists who use their senses to evaluate the appearance, aroma, taste, texture, and overall perception of chocolate. Through sensory evaluation, chocolate manufacturers can identify and address any sensory defects or undesirable characteristics in their products.For example, optimizing roasting conditions can reduce bitterness, sourness, and astringency in chocolate, leading to increased consumer liking. Additionally, research has shown that the sweetness and cocoa intensity of chocolate are positively correlated with consumer liking.
Sensory evaluation acts as a quality gatekeeper, ensuring that every product that reaches the consumer meets the highest standards of quality. Trained panelists are able to detect any off-flavors or off-odors that may be present in the chocolate. For example, if a batch of chocolate has been contaminated with mold, the panelists will be able to detect the musty aroma and advise the manufacturer to reject the batch. Similarly, sensory evaluations allow manufacturers to assess the texture of the chocolate, ensuring that it has a smooth and creamy mouthfeel. By addressing any sensory defects, chocolate manufacturers can ensure that their products consistently meet consumer expectations and deliver a satisfying sensory experience.
In addition to identifying potential defects, sensory evaluation can also provide valuable insights into the sensory properties that are most appreciated by consumers. This can help manufacturers to refine their recipes and processes to enhance these properties. For example, if consumers prefer a chocolate with a smooth, creamy texture, manufacturers can adjust their conching process to achieve this texture. If consumers prefer a chocolate with a rich cocoa aroma, manufacturers can adjust their roasting process to enhance this aroma. By using sensory evaluation to understand consumer preferences, manufacturers can create chocolates that are not only of high quality but also highly appealing to consumers.
Techniques Used in Sensory Analysis of Chocolate
Sensory analysis of chocolate involves the use of various techniques to understand and decode its sensory properties. Commonly employed methods include taste testing, where trained panelists evaluate chocolates with different basic tastes to understand their conscious and emotional responses.Another technique is flavor profiling, used to assess differences in melting, smoothness, cocoa, caramel, and aftertaste among different chocolate shapes. Time-intensity measurements help in understanding the impact of chocolate shape on cocoa flavor intensity. Together, these techniques provide valuable insights into the sensory characteristics of chocolate, guiding manufacturers to create products that meet consumers’ sensory expectations.
Taste testing is a fundamental technique used in the sensory analysis of chocolate. Trained panelists evaluate different chocolates and rate them based on their taste attributes such as sweetness, bitterness, sourness, and saltiness. This allows manufacturers to understand how these basic tastes contribute to the overall perception of the chocolate. For instance, if a chocolate is found to be too bitter, the manufacturer may adjust the formulation to reduce the bitterness and create a more balanced flavor profile. This approach ensures that manufacturers can create products that meet the diverse taste preferences of consumers.
Flavor profiling is another primary technique used in sensory analysis. It involves evaluating the different flavor attributes of chocolate, such as melting, smoothness, cocoa, caramel, and aftertaste. By profiling the flavors, manufacturers can gain a better understanding of the complex flavor profile of chocolate and use this information to create new and unique products. For example, if a certain chocolate shape is found to have a longer melting time and a more intense cocoa flavor, the manufacturer may choose to market it as a premium product with a rich and indulgent taste.
In contrast, time-intensity measurements are used to assess the impact of chocolate shape on cocoa flavor intensity. By measuring the intensity of the cocoa flavor over time, manufacturers can determine how the shape of the chocolate affects the release of flavors in the mouth. This information can be used to optimize the shape of the chocolate and create a more enjoyable sensory experience for the consumer. For instance, if a certain shape is found to result in a more intense cocoa flavor, the manufacturer may choose to use that shape for a product that is meant to deliver a bold and intense chocolate experience.
Factors Affecting Sensory Properties of Chocolate
Many factors influence the sensory properties of chocolate. These include the variety of cacao beans, fermentation process, roasting conditions, and conching process. Additionally, the presence of different basic tastes, such as sweetness, bitterness, sourness, and saltiness, can affect the taste of chocolate. Optimizing roasting conditions can reduce bitterness and astringency, leading to more acceptable chocolate. Notably, the shape of chocolate pieces can also impact texture and flavor perceptions, including differences in cocoa intensity.
The variety of cacao beans used in chocolate production can greatly influence its sensory properties. Different varieties of cacao beans have distinct flavor profiles, ranging from fruity and floral to nutty and earthy. The fermentation process also plays a significant role in developing the flavors of chocolate. During fermentation, microorganisms break down the sugars in the cacao beans, releasing compounds that contribute to the unique flavors of chocolate. The roasting process further enhances these flavors by developing Maillard reactions, which result in the characteristic chocolate aroma and taste.
Roasting conditions used in chocolate production can have a significant impact on its sensory properties. The duration and temperature of roasting can affect the level of bitterness and astringency in chocolate. By optimizing the roasting conditions, manufacturers can reduce these undesirable attributes and create a more enjoyable chocolate. Additionally, the conching process, which involves grinding and kneading the chocolate mass, can influence its texture and smoothness. Conching helps to refine the chocolate particles and distribute the cocoa butter evenly, resulting in a smooth and creamy texture.
The shape of chocolate pieces can also impact their sensory properties. Different shapes can create variations in texture and flavor perceptions. For instance, a chocolate bar may have a different mouthfeel compared to a chocolate truffle. The surface area and thickness of the chocolate can influence how it melts in the mouth and how the flavors are released. By carefully selecting the shape of the chocolate, manufacturers can create products that offer unique sensory experiences and cater to different consumer preferences.
The Science of Taste and Chocolate
- Sweetness and cocoa intensity are positively correlated with increased liking of chocolate.
- Bitterness, sourness, and astringency are negatively correlated with consumer liking.
- Different basic tastes in chocolate can evoke conscious and unconscious responses, influencing emotions and overall liking.
- Understanding the science of taste in relation to chocolate helps in creating products that cater to consumer preferences.
- The science of taste explores how taste buds perceive different flavors and how these flavors influence overall liking of food.
- Sweetness is a key taste attribute in chocolate, derived from sugars in cacao beans; its level can vary with the variety of cacao beans and amount of added sugar.
- Optimal level of sweetness can be understood to adjust formulation for creating a product that balances sweetness and bitterness.
- Cocoa intensity refers to the strength and richness of the cocoa flavor; a higher cocoa intensity is preferred for a more pronounced chocolate taste.
- Achieving desired cocoa intensity involves careful selection of cacao beans and the roasting process.
- Understanding the relationship between cocoa intensity and consumer liking aids in product formulation to meet consumer expectations.
- Bitterness in chocolate is caused by compounds like polyphenols; sourness can result from under-fermentation or improper processing; astringency is caused by tannins binding to proteins in the mouth.
- Minimizing undesirable taste attributes like bitterness, sourness, and astringency enables manufacturers to create a more enjoyable chocolate appealing to a wider range of consumers.